今天给大家讲解下如何安装LNMP ,首先呢我们要知道上面是DNF命令是什么.
DNF是什么?
DNF仅仅是基于RPM的Linux发行版(如CentOS、RHEL、Fedora等)的下一代包管理器(在YUM之后)。在本文中,我将向您展示如何使用DNF包管理器来管理CentOS 8包。接下来跟着我学习一步一步的学习吧。
DNF命令的一般语法
| 1 | dnf [Option] [Command] [Package_Name] |
DNF配置文件的位置
| 1 2 3 | Main Configuration: /etc/dnf/dnf.conf Repository: /etc/yum.repos.d/ Cache Files: /var/cache/dnf |
常用的DNF命令如下
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | +---------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Command | Description | +---------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |repolist | Display the configured software repositories | |install | Install a single or multiple packages on your system | |upgrade | Upgrade a package or packages on your system | |upgrade-minimal | Upgrade, but only 'newest' package match which fixes a problem that affects your system | |list | List a package or groups of packages | |info | Display details about a package or group of packages | |updateinfo | Display advisories about packages | |search | Search package details for the given string | |check-update | Check for available package upgrades | |remove | Remove a package or packages from your system | |reinstall | Reinstall a package | |downgrade | Downgrade a package | |autoremove | Remove all unneeded packages that were originally installed as dependencies | |distro-sync | Synchronize installed packages to the latest available versions | |makecache | Generate the metadata cache | |repository-packages | Run commands on top of all packages in given repository | |provides | Find what package provides the given value | |group | Display, or use, the groups information | |history | Display, or use, the transaction history | |clean | Remove cached data | |help | Display a helpful usage message | +---------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
YUM是什么?
Yum是使用RPM软件包管理器的Linux操作系统的免费开放源代码命令行软件包管理应用程序。
Yum是rpm的前端工具,可自动解决软件包的依赖性。它从发行官方存储库和其他第三方存储库安装RPM软件包。Yum允许您从系统中安装,更新,搜索和删除软件包。如果您想使系统保持最新,则可以通过yum-cron启用自动更新。此外,如果需要,它还允许您从yum更新中排除一个或多个软件包。
每个Linux发行版都有自己的软件包管理器,请单击下面的链接将其全部检出
YUM命令的常规语法
| 1 | yum [选项] [命令] [Package_Name] |
YUM配置文件的位置
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | 主要配置文件:/etc/yum.conf 其他存储库文件:/etc/yum.repos.d/ 缓存文件:/ var / cache / yum 日志文件:/var/log/yum.log Yum插件配置:/etc/yum/pluginconf.d/ /etc/yum/version-groups.conf |
DNF和YUM的区别,为什么用DNF代替YUM?
在centos 8以前的版本中我们经常是使用的是yum命令进行安装,如今现在linux centos系列的最新系统centos 8把dnf命令作为核心命令,也就是所你不用安装dnf就可以使用他了,那么为什么centos 8建议你使用dnf呢?
DNF和YUM的区别
Yum软件包管理器已由 DNF软件包管理器代替,因为Yum中许多长期存在的问题仍未解决。
这些问题包括性能不佳,内存使用过多,依赖性解析速度变慢。
DNF使用“ libsolv”进行依赖关系解析,由SUSE开发和维护以提高性能。
通过下面表我们可以看到是DNF和YUM的最大区别。
| 序号 | DNF (Dandified YUM) | YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) |
| 1 | DNF使用libsolv进行依赖项解析,由SUSE开发和维护。 | YUM使用公共API进行依赖项解析 |
| 2 | API已完全记录 | API尚未完全记录 |
| 3 | 它是用C,C ++,Python编写的 | 它仅用Python编写 |
| 4 | DNF当前在Fedora,Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8(RHEL),CentOS 8,OEL 8和Mageia 6/7中使用。 | YUM当前用于Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6/7(RHEL),CentOS 6/7,OEL 6/7。 |
| 5 | DNf支持各种扩展 | Yum仅支持基于Python的扩展 |
| 6 | 该API有充分的文档记录,因此可以轻松创建新功能 | 由于没有正确记录API,因此很难创建新功能。 |
| 7 | 同步存储库的元数据时,DNF使用较少的内存。 | 在同步存储库的元数据时,YUM使用过多的内存。 |
| 8 | DNF使用可满足性算法来解决依赖关系解析(它使用字典方法来存储和检索包及依赖关系信息)。 | 由于公共API,Yum依赖项解析变得缓慢。 |
| 9 | 就内存使用率和存储库元数据的依存关系解析而言,所有性能都很好。 | 总体而言,许多方面的表现都很差。 |
| 10 | DNF更新:如果软件包在DNF更新过程中包含无关的依赖项,则不会更新该软件包。 | YUM将更新软件包而不进行验证。 |
| 11 | 如果启用的存储库没有响应,则dnf将跳过它并继续使用可用存储库进行事务。 | 如果存储库不可用,则YUM将立即停止。 |
| 12 | dnf更新和dnf升级相等。 | YUM就不同了 |
| 13 | 软件包安装的依赖关系未更新 | YUM为这种行为提供了一个选择 |
| 14 | 清理软件包删除:删除软件包时,dnf会自动删除用户未明确安装的所有依赖软件包。 | YUM没有这样做 |
| 15 | Repo Cache更新计划:默认情况下,系统启动后十分钟,dnf每小时检查一次已配置存储库的更新。此操作由名为“ /usr/lib/systemd/system/dnf-makecache.timer”的系统计时器单元控制。 | YUM也这样做。 |
| 16 | 内核软件包不受dnf保护。与Yum不同,您可以删除所有内核程序包,包括正在运行的程序包。 | Yum不允许您删除正在运行的内核 |
| 18 | DNF包含29k行代码 | Yum包含56k行代码 |
| 19 | DNF由Ales Kozumplik开发 | YUM由Zdenek Pavlas,Jan Silhan和团队成员开发 |
通过上面的数据对比我想你一定会爱上DNF的操作的,好吧接下来呢就让我带领你学习在centos 8安装安装最新版的LNMP(Linux+Nginx+MariaDB+PHP)吧。
安装Nginx
首先你要使用超级用户安装这些软件,不然的话没有权限,普通用户切换超级用户命令
| 1 | su - |
或者使用sudo前缀进行操作,例如:
| 1 | sudo dnf -y install http://nginx.org/packages/centos/8/x86_64/RPMS/nginx-1.16.1-1.el8.ngx.x86_64.rpm |
接下来的所有命令操作我都是以超级用户root权限进行的,后续不再赘述,请注意。
通过dnf在线安装最新的版本:
| 1 | dnf -y install http://nginx.org/packages/centos/8/x86_64/RPMS/nginx-1.16.1-1.el8.ngx.x86_64.rpm |
如果你没有联网,那么你可以通过上传RPM包到你的服务器,然后通过离线安装就是用下面的命令:
| 1 | dnf localinstall package-1.2.3.rpm |
如果你想自定义安装其他的nginx的版本可以打开官网:http://nginx.org/packages/centos/8/x86_64/RPMS/进行查看如下:
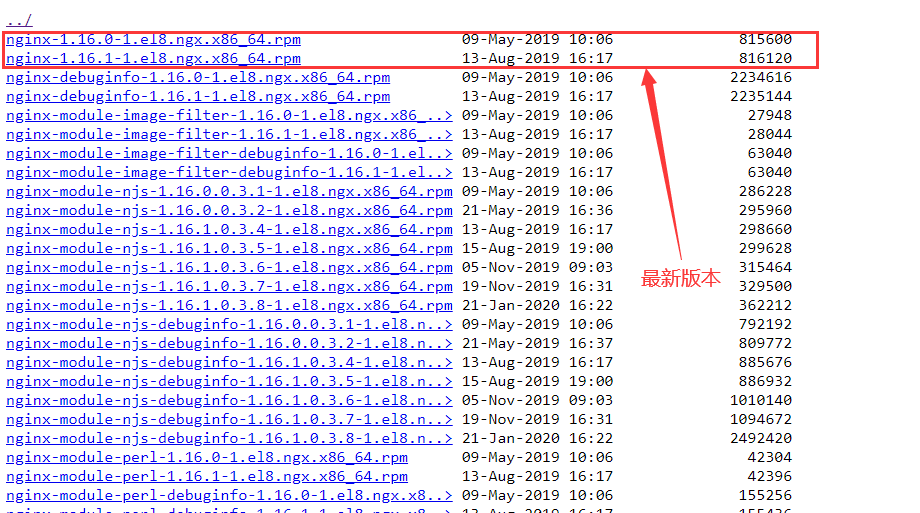
你想安装其他版本可以dnf -y install http://nginx.org/packages/centos/8/x86_64/RPMS/后面再跟包名即可:nginx-1.16.1-1.el8.ngx.x86_64.rpm
nginx-1.16.1-1.el8.ngx.x86_64.rpm:表示就是包的名字。
安装完成后查看版本号,重启,开机启动设置
查看nginx版本
| 1 2 3 | [root@localhost ~]# nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.16.1 [root@localhost ~]# |
查看状态是否启动了,刚安装的后的nginx默认是没有激活的,查看状态
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | [root@localhost ~]# systemctl status nginx ● nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.d └─php-fpm.conf Active: inactive (dead) since Sun 2020-03-15 12:11:32 CST; 1s ago Docs: http://nginx.org/en/docs/ Process: 37713 ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 32448 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Mar 14 22:57:35 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting nginx - high performance web server... Mar 14 22:57:35 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started nginx - high performance web server. Mar 15 12:11:31 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Stopping nginx - high performance web server... Mar 15 12:11:32 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Stopped nginx - high performance web server. [root@localhost ~]# |
启动开机,开机的时候启动命令
| 1 2 | systemctl start nginx systemctl enable nginx |
再次查看状态
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | [root@localhost ~]# systemctl status nginx ● nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.d └─php-fpm.conf Active: active (running) since Sun 2020-03-15 12:12:40 CST; 55s ago Docs: http://nginx.org/en/docs/ Main PID: 37738 (nginx) Tasks: 2 (limit: 16700) Memory: 2.5M CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service ├─37738 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf └─37739 nginx: worker process Mar 15 12:12:39 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting nginx - high performance web server... Mar 15 12:12:40 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started nginx - high performance web server. [root@localhost ~]# |
在检查下在浏览器是否能够打开,在安装nginx激活开启后我们还需要执行如下几个步骤:
第一步:查看我们的防火墙是否设置端口屏蔽如果是no则需要添加端口号,因为我们的网站是80 或者443端口,所以最后这两个都开启
| 1 2 3 | [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --query-port=80/tcp no [root@localhost ~]# |
第二步:永久开启开启80和443端口
| 1 2 3 4 5 | [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp secucessfull [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=443/tcp secucessfull [root@localhost ~]# |
第三步:重新reload配置一下防火墙
| 1 | firewall-cmd --reload |
第四步:执行 下面的命令查看ip,使用浏览器访问服务器ip。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | [root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens3: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.118.150 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.118.255 ...... ...... ...... |
既是inet 对应的ip 192.168.118.150,访问后如下图。
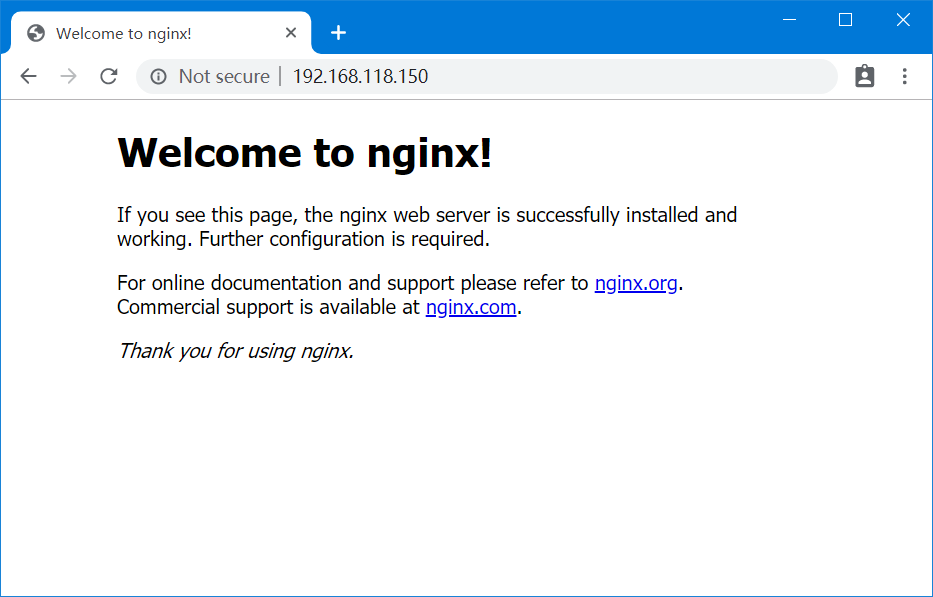
安装nginx完成ok。
安装PHP7.4
PHP是PHP超文本预处理程序的递归首字母缩写,是一种流行的服务器端脚本语言,用于创建功能强大的动态网站。
在本文中,您将学习如何在CentOS 8 Linux上安装PHP 7.4。
步骤1:添加EPEL和Remi存储库
首先,您需要添加EPEL和Remi存储库,以便能够在CentOS 8 Linux上安装PHP 7.4。要在CentOS 8上安装和启用EPEL存储库,请执行以下dnf命令。
| 1 | dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 | [root@localhost ~]# dnf install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm Last metadata expiration check: 1:06:39 ago on Sat 14 Mar 2020 10:50:45 PM CST. remi-release-8.rpm 5.8 kB/s | 23 kB 00:03 Dependencies resolved. ============================================================================================== Package Architecture Version Repository Size ============================================================================================== Installing: remi-release noarch 8.1-2.el8.remi @commandline 23 k Upgrading: centos-release x86_64 8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8 BaseOS 21 k Installing dependencies: centos-gpg-keys noarch 8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8 BaseOS 11 k centos-repos x86_64 8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8 BaseOS 12 k Transaction Summary ============================================================================================== Install 3 Packages Upgrade 1 Package Total size: 67 k Total download size: 44 k Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: (1/3): centos-repos-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64.rpm 24 kB/s | 12 kB 00:00 (2/3): centos-release-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64.rpm 37 kB/s | 21 kB 00:00 (3/3): centos-gpg-keys-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.noarch.rpm 14 kB/s | 11 kB 00:00 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 25 kB/s | 44 kB 00:01 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Running scriptlet: centos-gpg-keys-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.noarch 1/1 Installing : centos-gpg-keys-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.noarch 1/5 Installing : centos-repos-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64 2/5 Upgrading : centos-release-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64 3/5 Installing : remi-release-8.1-2.el8.remi.noarch 4/5 Cleanup : centos-release-8.0-0.1905.0.9.el8.x86_64 5/5 Running scriptlet: centos-release-8.0-0.1905.0.9.el8.x86_64 5/5 Verifying : centos-gpg-keys-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.noarch 1/5 Verifying : centos-repos-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64 2/5 Verifying : remi-release-8.1-2.el8.remi.noarch 3/5 Verifying : centos-release-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64 4/5 Verifying : centos-release-8.0-0.1905.0.9.el8.x86_64 5/5 Upgraded: centos-release-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64 Installed: remi-release-8.1-2.el8.remi.noarch centos-gpg-keys-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.noarch centos-repos-8.1-1.1911.0.8.el8.x86_64 Complete! [root@localhost ~]# |
同样,要验证Remi存储库是否存在,请运行该命令。
| 1 | rpm -qa | grep remi |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | [root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa | grep remi php-xml-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-json-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-cli-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 remi-release-8.1-2.el8.remi.noarch php-common-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-opcache-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-sodium-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-fpm-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-pdo-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 php-mbstring-7.4.3-1.el8.remi.x86_64 [root@localhost ~]# |
步骤2:在CentOS 8上安装PHP 7.4
当你完成成功添加EPEL和Remi存储库后,执行下面的命令以获得可用PHP模块列表。
| 1 | dnf module list php |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | [root@localhost ~]# dnf module list php Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:25 ago on Sun 15 Mar 2020 10:14:27 AM CST. CentOS-8 - AppStream Name Stream Profiles Summary php 7.2 [d] common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language php 7.3 common, devel, minimal PHP scripting language Remi's Modular repository for Enterprise Linux 8 - x86_64 Name Stream Profiles Summary php remi-7.2 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language php remi-7.3 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language php remi-7.4 common [d], devel, minimal PHP scripting language Hint: [d]efault, [e]nabled, [x]disabled, [i]nstalled [root@localhost ~]# |
步骤3:我们通过上面可以看到有两个库的php版本,那么我们需要安装php7.4,所以要选择最后一个remi版本的,接下来我们正式安装php7.4
| 1 | dnf module enable php:remi-7.4 |
步骤4:一旦启用了PHP remi-7.4模块,就可以使用下面的命令继续安装PHP。这还将安装许多其他包,如Apache和Nginx模块。
| 1 | dnf install php php-cli php-common |
步骤5:要检查安装的PHP版本,请运行该命令,完成。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | [root@localhost ~]# php -v PHP 7.4.3 (cli) (built: Feb 18 2020 11:53:05) ( NTS ) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v3.4.0, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v7.4.3, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies [root@localhost ~]# |
通过上面我们可以地看到已经安装好了PHP 7.4!现在可以继续使用PHP测试和部署应用程序,接下来我们来安装数据库MariaDB
安装MariaDB
第一步:安装数据库MariaDB
| 1 2 | dnf install boost-program-options dnf install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client --disablerepo=AppStream |
当你执行上面的命令后出现下面,并按下 Y 键进行安装
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | MariaDB 186 kB/s | 489 kB 00:02 Last metadata expiration check: 0:00:01 ago on Sat 04 Jan 2020 08:37:41 PM EAT. Dependencies resolved. ======================================================================================================================================================== Package Arch Version Repository Size ======================================================================================================================================================== Installing: MariaDB-client x86_64 10.4.11-1.el8 mariadb 12 M MariaDB-server x86_64 10.4.11-1.el8 mariadb 26 M Installing dependencies: MariaDB-common x86_64 10.4.11-1.el8 mariadb 87 k galera-4 x86_64 26.4.3-1.rhel8.0.el8 mariadb 13 M Transaction Summary ======================================================================================================================================================== Install 4 Packages Total download size: 51 M Installed size: 196 M Is this ok [y/N]: y |
2.第二步:开启并开机启动数据库MariaDB service
| 1 | systemctl enable --now mariadb |
查看运行的状态如下
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | systemctl status mariadb ● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.4.11 database server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d └─migrated-from-my.cnf-settings.conf Active: active (running) since Sat 2020-01-04 20:40:50 EAT; 15s ago Docs: man:mysqld(8) https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/ Main PID: 31317 (mysqld) Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..." Tasks: 30 (limit: 11512) Memory: 73.4M CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service └─31317 /usr/sbin/mysqld Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] InnoDB: 10.4.11 started; log sequence number 60972; transaction id 21 Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] InnoDB: Loading buffer pool(s) from /var/lib/mysql/ib_buffer_pool Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] InnoDB: Buffer pool(s) load completed at 200104 20:40:50 Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] Plugin 'FEEDBACK' is disabled. Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] Server socket created on IP: '::'. Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] Reading of all Master_info entries succeeded Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] Added new Master_info '' to hash table Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: 2020-01-04 20:40:50 0 [Note] /usr/sbin/mysqld: ready for connections. Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal mysqld[31317]: Version: '10.4.11-MariaDB' socket: '/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock' port: 3306 MariaDB Server Jan 04 20:40:50 centos8.novalocal systemd[1]: Started MariaDB 10.4.11 database server. |
3.第三步:数据库安全设置
好了,现在我们对MariaDB 10.4已经安装在CentOS 8上,通过运行mysql_secure_installation命令来保护它。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 | mysql_secure_installation NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY! In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank, so you should just press enter here. Enter current password for root (enter for none): OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation. Set root password? [Y/n] y New password: Re-enter new password: Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y ... Success! Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y ... Success! By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Dropping test database... ... Success! - Removing privileges on test database... ... Success! Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y ... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB! |
4.第四步:测试访问数据库。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | mysql -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 19 Server version: 10.4.11-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT version(); +-----------------+ | version() | +-----------------+ | 10.4.11-MariaDB | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> QUIT Bye |
ok,通过上面我们已经学习完成安装好了数据库,以及所有的web服务LNMP软件,希望对你有帮助。

503 Service Temporarily Unavailable 怎么解决,我看wp、dz官网都有这错误
你安装的是怎么安装的,使用的的是dnf吗?
文章不错非常喜欢